Protecting your legacy in the Peace Garden State.
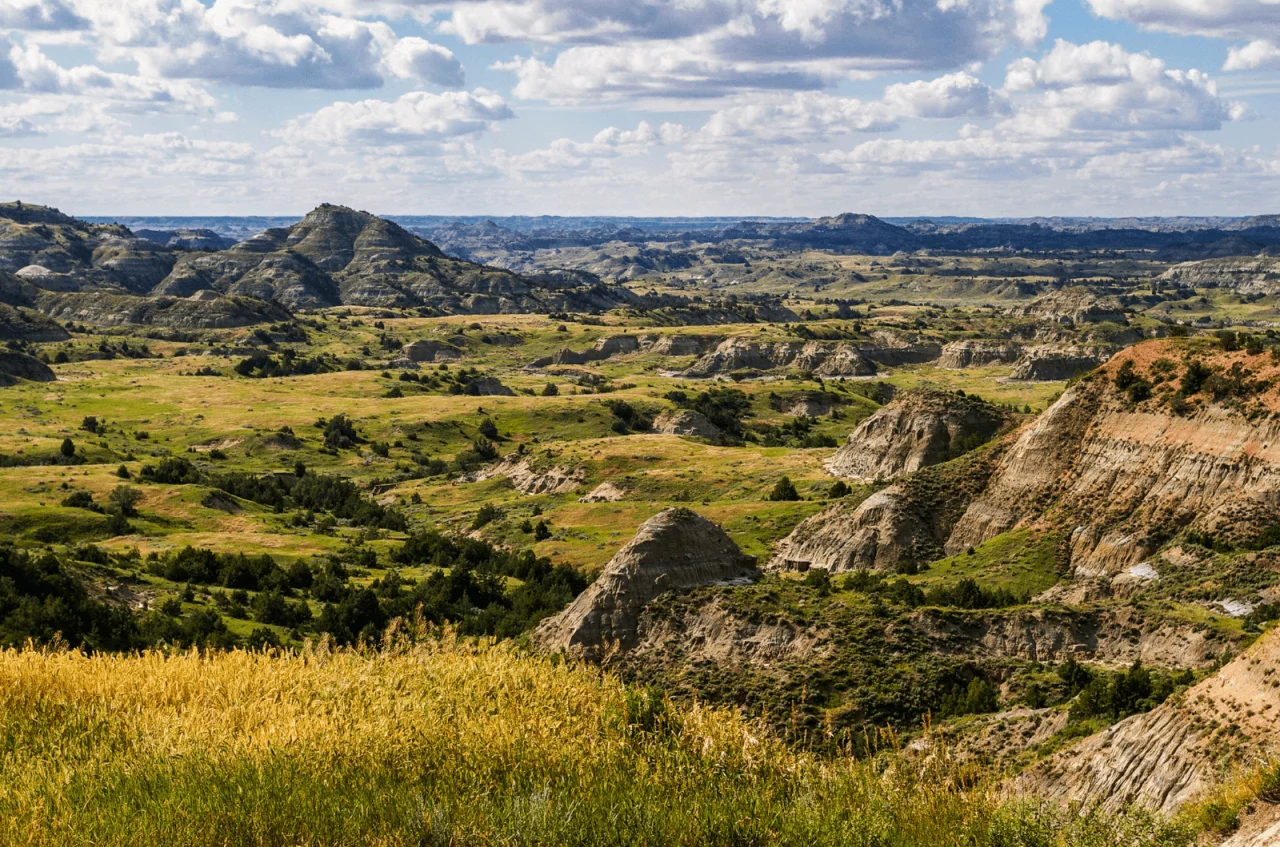
Imagine a future where your life’s work is passed on exactly as you envisioned, where your loved ones are cared for, and where your values live on through your estate. That’s the promise of estate planning. In North Dakota, where wide-open landscapes mirror the sense of independence many families treasure, estate planning takes on unique features that deserve careful attention.
It’s more than just a will; it’s a plan that protects your assets, honors your wishes, and spares your family from unnecessary stress.
Understanding the Basics
Estate planning is about arranging your affairs so your property is managed and distributed the way you want, during your lifetime and after. In North Dakota, an effective plan can:
- Ensure your assets are distributed as you wish
- Reduce taxes and liabilities on your estate
- Protect beneficiaries, including minors
- Minimize disputes and legal challenges
- Appoint guardians for children
- Plan for incapacity through health care directives
The right documents give you peace of mind and make things easier for your family.
Key Estate Planning Terms
- Executor: Carries out your will and manages the estate.
- Beneficiary: Anyone designated to inherit from your estate or trust.
- Trustee: Manages assets held in a trust for beneficiaries.
- Probate: The court process of validating a will and administering an estate.
- Intestate: Dying without a will; the state decides how assets are distributed.
- Living Will: States your medical treatment preferences.
- Power of Attorney (POA): Lets someone act on your behalf in financial or health matters.
- Codicil: A formal amendment to an existing will.
Building an Estate Plan
A strong estate plan in North Dakota often follows these steps:
- Assess and document all assets and liabilities.
- Define your priorities, whether that’s reducing taxes, protecting children, or supporting charities.
- Select the right tools, such as wills, trusts, and POAs.
- Draft documents with legal guidance.
- Review and update your plan regularly to reflect changes in your life or the law.
This process ensures your plan stays current and effective.
Transferring an Estate in North Dakota
When someone passes away, estate transfer usually involves probate. This is where the court validates the will and oversees the distribution of assets.
- If there’s a will: The executor manages the process.
- If there’s no will (intestate): Assets are distributed under state law, typically to close relatives.
- Simplified probate: Available for smaller estates, making the process quicker and less costly.
- Transfer-on-death deeds and beneficiary designations: Can allow certain assets to bypass probate entirely.
Understanding these tools helps streamline the process and reduce expenses.
Essential Transfer Documents
- Deeds for real estate (e.g., warranty or quitclaim deeds)
- Titles for vehicles and other registrable property
- Powers of Attorney for financial management
- Last Will and Testament
- Death certificate
- Asset inventory
- Trust agreements (if applicable)
- Beneficiary designations on accounts and policies
Having these documents ready ensures smoother asset transfers and compliance with state law.
Financial Powers of Attorney
A Financial POA authorizes someone to manage your money if you can’t. This person may:
- Pay bills
- Manage investments
- Handle property transactions
Choose your agent wisely – they should be trustworthy and financially capable. Discuss expectations clearly to ensure they act in your best interest.
Wills
A will remains one of the most important estate planning tools. In North Dakota, a valid will must be:
- Written
- Signed by the testator
- Witnessed by at least two people
Wills should specify beneficiaries, name an executor, and may include guardianship provisions for minor children. Reviewing and updating your will regularly keeps it aligned with your current wishes.
Trusts
Trusts provide flexibility, privacy, and tax advantages. Common types include:
- Revocable Living Trusts: Can be changed during your lifetime.
- Irrevocable Trusts: Permanent but useful for tax planning and creditor protection.
- Testamentary Trusts: Created through a will and activated after death.
Trusts can help avoid probate, shield assets, and provide long-term support for beneficiaries.
Health Care Decisions
Estate planning isn’t just about money – it’s also about health care. In North Dakota, key tools include:
- Health Care Directive (Living Will): States your treatment preferences.
- Medical Power of Attorney: Names someone to make medical decisions for you.
These documents protect your autonomy and relieve loved ones of uncertainty during stressful times.
Summary
Estate planning in North Dakota requires careful thought and the right tools. Key steps include:
- Drafting a valid will
- Using trusts to protect assets and minimize taxes
- Establishing financial and medical powers of attorney
- Preparing transfer documents like deeds and titles
- Understanding probate procedures, including simplified options
- Reviewing your plan regularly to reflect life changes
By planning ahead, you protect your family, reduce legal stress, and secure your legacy for generations to come.